
Have you seen the Multiple choice questions Meme on Social Media? Or attempted the multiple-choice options in your exams?
Oh well! Are they all same or different?
We can agree it’s all Steve Harvey. Yet all four images are different!
Say we pick the option ‘d’ as the original version Harvey.
Google faces a similar dilemma when it comes across various similar pages on your website with the same content and it has to choose the relevant link for a search query to display in the results.
If you want to make things easy and also want a specific URL to rank, then you have to mark that URL as something called a canonical URL in SEO. It’s like we picked option d as the true version of Harvey.
But what do I mean by similar pages and why do they occur? I have explained it in this article along with what a canonical URL means and why you should be using it.
Read on for a better understanding.
What is a canonical URL in SEO?
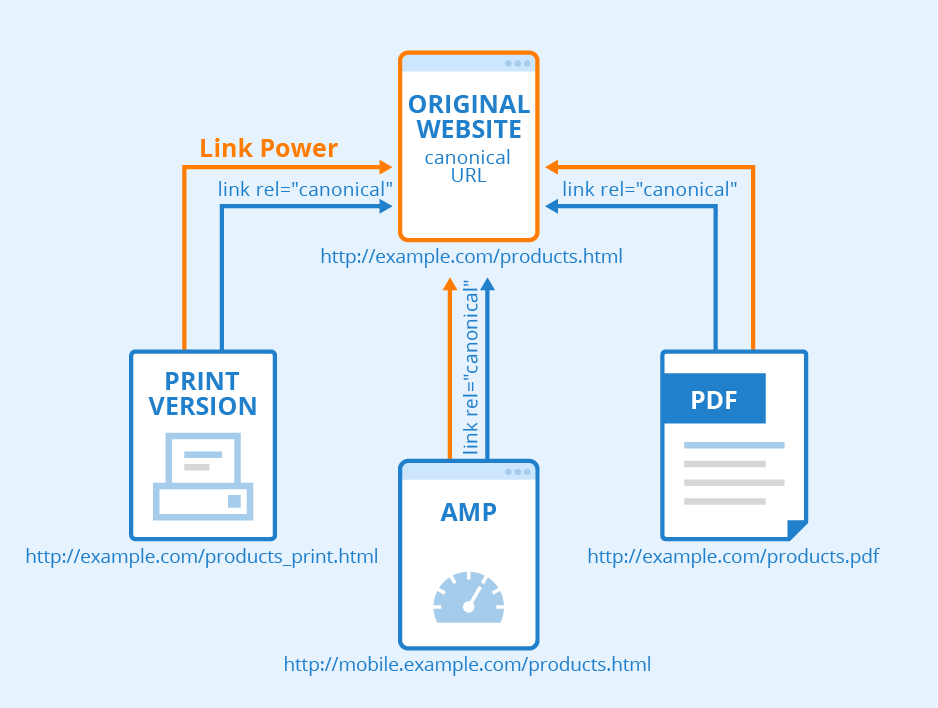
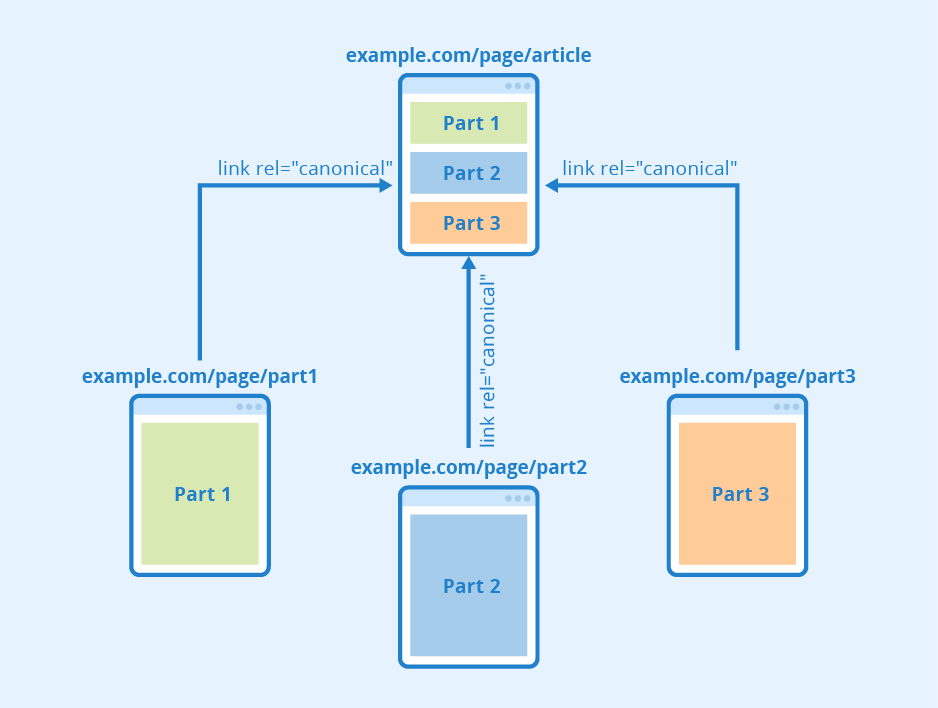
A canonical URL is a way of specifying a URL that is the primary or the master copy of a page when there are duplicate pages. The canonical element of the URL informs Google and other search engines to crawl and index the page with the specified URL.
What are duplicate pages?
When I say duplicate pages or content I do not mean plagiarized or copied content. It means duplicate pages within a website. Duplicate content can be of two types.
- A single page accessible by multiple URLs ( a page with mobile and desktop versions)
- Different pages with similar content (an eCommerce site with various options for the same product – sorted by item color or price).
When there are duplicate versions of the same page, then Google chooses one of them to be the representative form as the canonical version to crawl it. The duplicate pages are crawled less.
A canonical tag (rel=canonical) is used to mark a page as a canonical URL to inform the same to Google.
But before you understand marking a canonical tag and how to use them, you need to know why duplicate content exists in the first place.
Why does duplicate content exist?
The Content Management Systems of today allow multiple URLs to launch the same content. No one intentionally creates duplicate pages.
It happens when there are different versions of a site that are indexable, there are alternate versions for different device types (mobile or desktop), or there are dynamic URLs.
Look at the links below.
- http://example.com
- https://www.example.com
- http://www.example.com
- https://m.example.com
- https://www.example.com/index.php
Another situation where this occurs is in eCommerce websites. Suppose there is a variety of options for the same product (like different colors or types).
Each type has a different URL with practically the same content. This causes multiplicity.
To you and me they look the same, but a search bot reads each of them as a unique URL even if there is minor variations.
When there are similar or duplicate pages Google tries to identify and mark one of them as a canonical URL and crawl it more frequently than the other pages. But if Google can choose a canonical URL by itself, why should you?
Why should you use canonical URL in SEO?
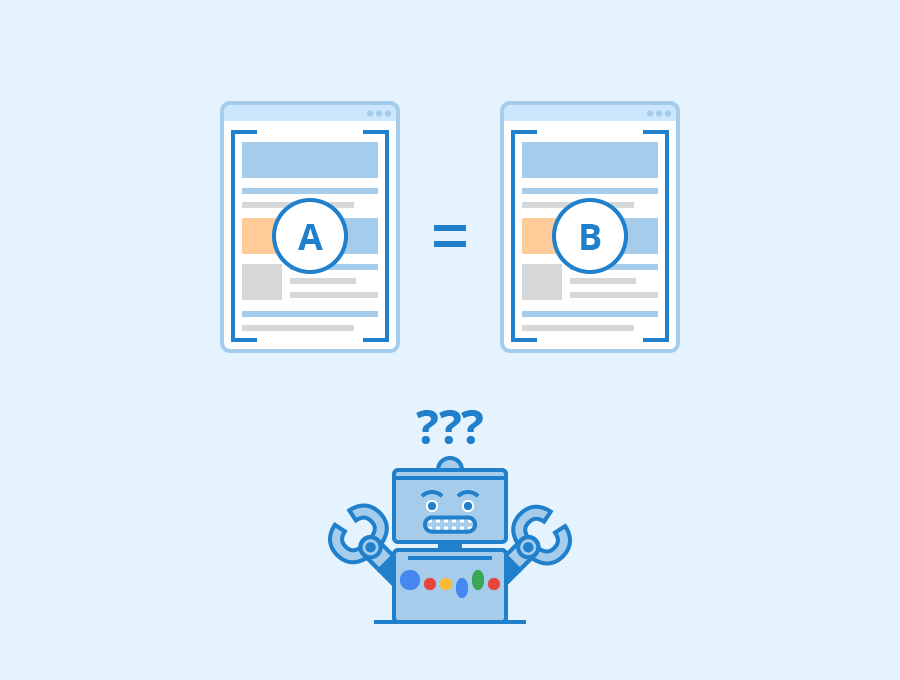
Duplicate content confuses Google (and other search engines). It would have to make a decision on
- Which of the similar pages should be indexed
- Which of the pages should be ranked as relevant for suitable queries
- Whether it should prioritize and pick one, or choose all equitably?
When you have not used canonical URLs you are leaving it to Google to pick on the URLs, it will either choose one or crawl both, which may not really work favorably for you.
If you want users to be able to access all the versions of the page URL while you also want to index just one of them, then you need to canonicalize the URL that you wish to be indexed.
Choosing a canonical URL among duplicate or similar ones has several other advantages, such as:
1 – You can specify which URL you want people to see in search results.
2 – Using canonical URLs helps simplify and organize your pages. When there are multiple URLs, it is difficult to track the performance metrics of the content.
3 – You can consolidate link signals for duplicate content. The information of the individual duplicate URLs is merged into one primary URL. Also, similar or duplicate content will not be competing for ranking in the search results.
4 – You can manage syndicated content. If you are syndicating your content to publish on other domains, you can choose your preferred URL for page ranking.
5 – You can save on the crawl budget by preventing crawlers from spending time on duplicate pages.
6 – It can help prevent duplicate content from affecting your site’s performance.
Now that we know that canonical URLs have a purpose in SEO, let us see how to set them on a WordPress website.
How to set a canonical URL on WordPress?
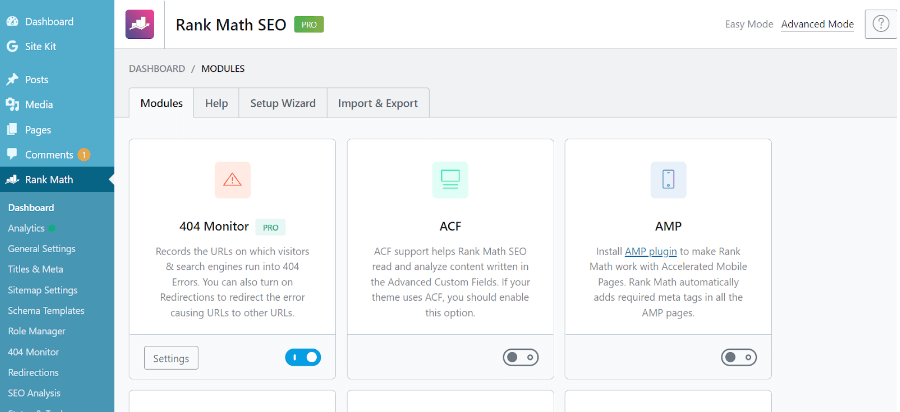
Life is n times easier with WordPress and its plugins. My go-to plugin for most SEO things is Rank Math.
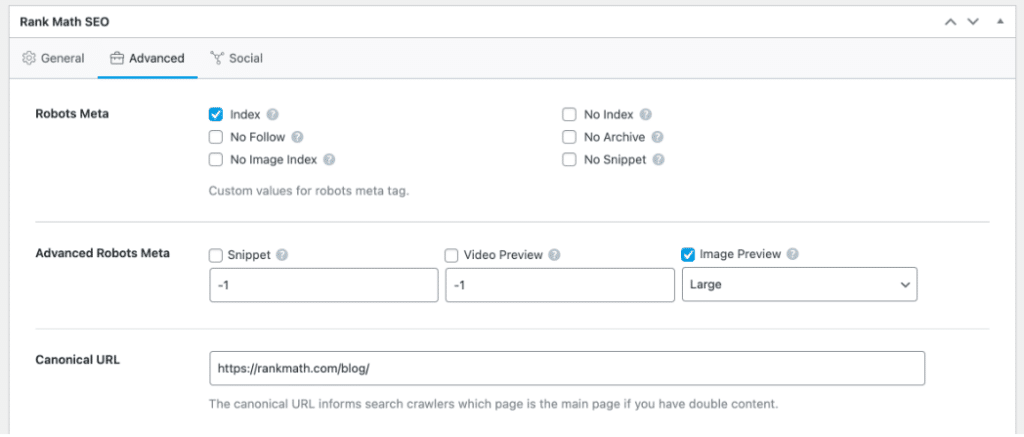
To set a canonical URL for a page or post, head to your Rank Math settings. In the ‘Advanced’ tab of the Rank Math meta box, you should find a field to add your canonical URL.
Setting canonical URL using Yoast SEO
Just like in Rank Math, Yoast SEO offers you an option of adding the canonical URL in its advanced settings.
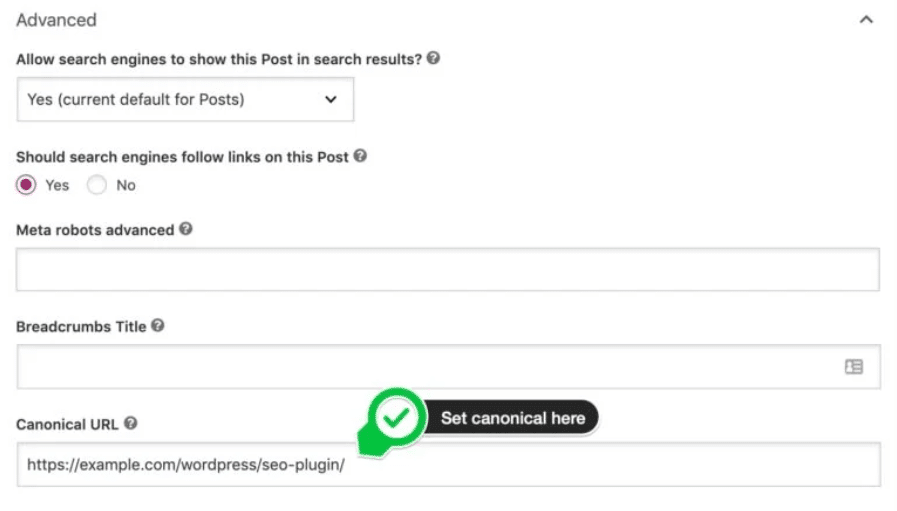
When you are adding canonical URLs to your pages you need to keep in mind some of the good practices for SEO purposes.
Canonical tags – Best practices for SEO
You can follow some
- Use absolute URLs with the complete domain name (complete with the https, www, and all).
- Use lowercase URLs. Search engines see lowercase and uppercases differently.
- Use the correct version of the domain: whether it is http or https
- Use a single canonical URL for a page.
- Use self-referential canonical URL.
- Use Sitemap to select a canonical URL
It is important to note that canonicals are not directives to the search engines but mere signals to indicate that the selected URL can be chosen for ranking. The search engines may or may not consider them.
There is only so much you can do. In spite of following the guidelines, it is still likely that you may face issues here. But don’t you worry! You can find and fix them.
How to find and fix issues with canonical URLs?
The most direct way of finding issues is by searching every possible version of your site’s URL on the search engine. If all the URLs redirect to one version, then there are no canonical issues. But clearly, this method is tedious.
Finding canonical URLs is easier with the Site Audit tools like Ahrefs or SEMrush.
These tools help find all duplicate content on your site and related canonical issues and produce a report for your understanding.
How do you fix the issues?
There are a few ways by which you can fix canonical issues based on what causes them.
- By canonicalizing all the pages on your site. This resolves the issue with the URLs that are changed by user interaction.
- By implementing 301 redirects for duplicate pages throughout your site. This helps with the duplicates caused by https vs http and www vs non-www.
- By ensuring that other site use canonical tags when publishing content from your site. This resolves issues with the syndicated content causing duplicate URLs across multiple sites.
- By referring duplicate pages to the preferred URL using canonical tags. This resolves the duplicate URLs caused by changes in the device or Amped pages.
Conclusion
So that was about canonical URLs and their use. The terminology makes it sound new and complicated. But in reality, it isn’t.
Gone are the days of struggling with coding. The tools available today enable even beginners to comfortably work with websites and their maintenance.
At the same time, it is important to learn to use the tools and the features right or things could go south.
I have tried to simplify the seemingly difficult subject of canonicalization. Have I missed anything?
Let me know in the comments.
FAQs
What is a canonicalized URL?
Canonicalized URL is the URL that best represents a set of similar/duplicate content. Canonicalization is the process of picking such a URL for Google to crawl and index.
How do I know that I have duplicate content?
You can use tools like Ahrefs, SEMrush, or Moz to audit your site. These tools scan your website and provide a report on its performance and any occurring issues.
If your site has issues with duplicate content, it should show.
When to use a canonical URL?
When you want users to be able to access all versions of a page but only one of them should be indexed by the search engine, you should use a canonical URL.
What is a non-canonical URL?
A non-canonical URL is a URL that is different from the chosen canonical URL and can mislead a search engine as they index pages that have an address different from their canonical versions.
What is the difference between a canonical tag and a redirect?
A redirect is a directive to the search engine to go to another page while a canonical tag is a hint that the selected URL is the primary one.
It is necessary to note that Google may or may not consider the tagged canonical URL.


