
Key Takeaways for you
| – Cloaking in SEO is a technique used by webmasters where different content is shown to Google and human visitors. – Cloaking is done for a lot of reasons. It is mostly when a website wants to use a lot of visual elements and less text on its web pages which Google does not approve of. – Hidden texts, User agent cloaking, IP Address cloaking, HTTP accept-language cloaking, HTTP_Referer cloaking, Java Script cloaking, and Flash pages are all types of cloaking in SEO. – Cloaking is a black hat technique and if caught Google can penalize you, ban your site, or ruin your brand name. – To detect cloaking you can analyze the website’s source code or by comparing SERP results to an actual web page. – You can also use online cloak checkers or look for other signs such as low-quality content or keyword stuffing. |
Camouflaging in nature is cryptic coloration used by animals to hide and defend themselves from predators. The same goes for army personnel who use it to protect themselves and their equipment from enemies.
But camouflaging in SEO has nothing defensive about it.
It is in fact an offense.
The term used is cloaking.
How is cloaking used in SEO? Why is it an offense?
Read on to understand.
What is cloaking in SEO?
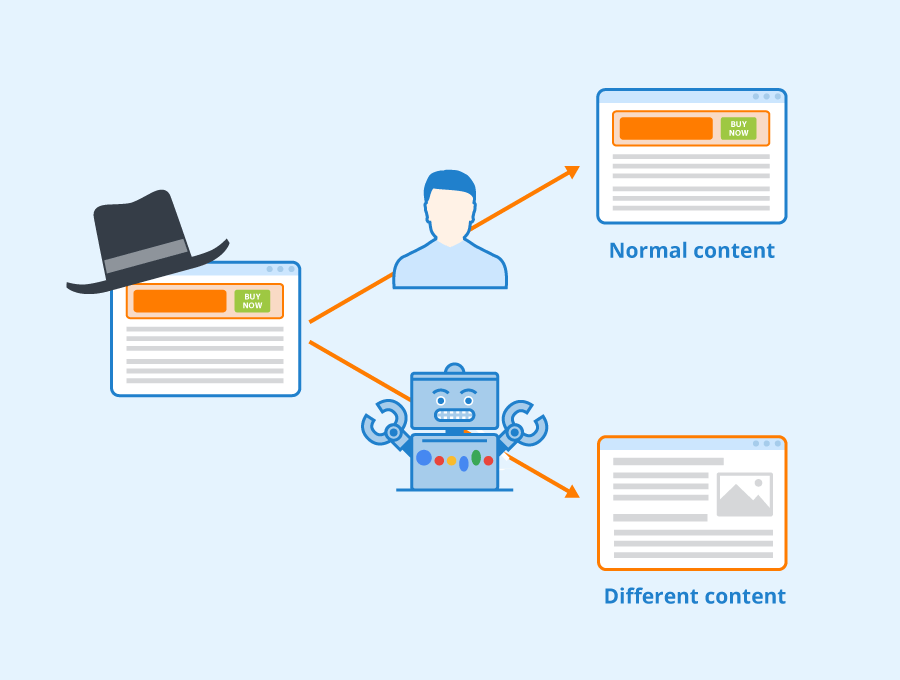
Cloaking in general means hiding something from someone. Cloaking in SEO is a technique used by webmasters where different content is shown to Google and human visitors.
For example, consider a beauty product brand.
A false reality is created to mask the content from the crawlers and up the web page rankings in the SERP by misleading the crawlers.
For example, users may see a lot of graphic or multimedia content with little text on a web page, while the same is presented with different content like HTML code or text that is optimized for search engines, though with the same URL.
Cloaking is done for a lot of reasons. It is mostly when a website wants to use a lot of visual elements and less text on its web pages which Google does not approve of. Cloaking is an easy way out to do what you want while deceiving Google by making it seemingly rule-abiding.
If it is something that needs to be hidden then it is probably wrong. It is also a violation of search engine guidelines and subject to penalty with the website being permanently removed from the search engine index.
In the SEO world, such practices are called black hat SEO.
But sometimes cloaking can happen accidentally too. It is better that you know how these things happen, how to avoid them, and what you need to do if you know it has happened to your website.
Let us begin with understanding the different types of cloaking.
What are the different types of cloaking?
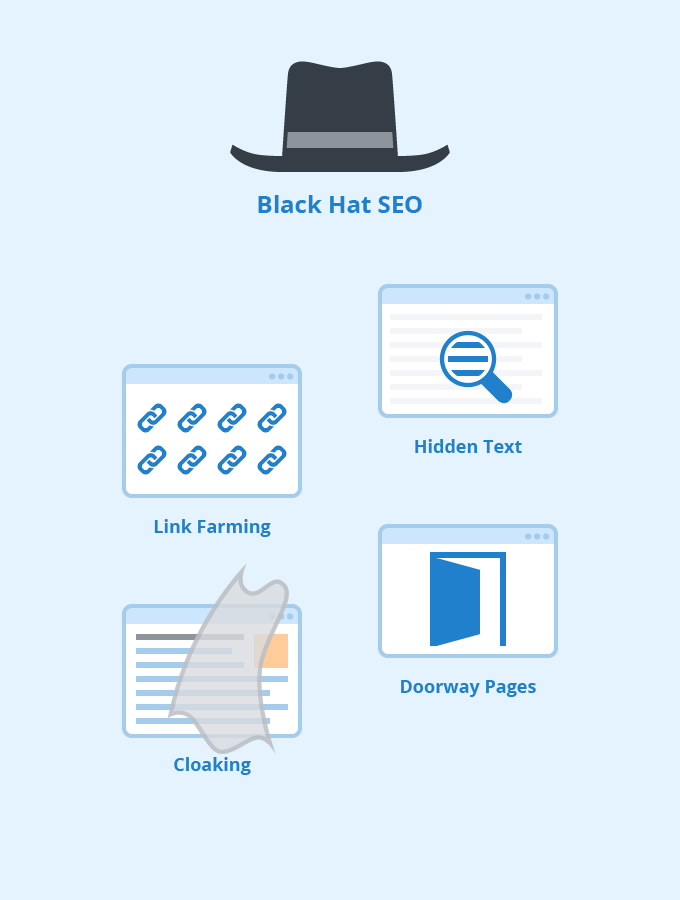
Technically speaking the code to HTML shown to users and crawlers are each different. There are several ways that cloaking occurs and all are against the search engine guidelines. Here are some examples of the most common types of cloaking practices.
Hidden text:
Website owners implement hidden text on various web pages in an attempt to deceive search engines. This is usually done by making the text color the same as the background color. Similar means are used to overwrite text and employ keyword stuffing so that the web page ranks in SERPs.
User Agent Cloaking:
User agents are applications like web browsers or automated programs. In user-agent cloaking, a designated user agent is used in place of traditional users to evaluate the type of visitors on the page to determine which version of the web page needs to be presented (or cloaked). The designated user agent is a code that is sent directly to the web server. When a bot or crawler visits the web page, specially prepared content is shown to it.
IP Address Cloaking
This is a very common form of cloaking where a web server delivers specific content based on the IP address of the visitor. Every user has his or her own IP address which is based on their location and internet service provider.
This is done by using reverse DNS records to identify the IP address. A .htaccess is set up to redirect the users to a desired page with a good SERP ranking.
HTTP Accept language cloaking
In this type of cloaking a user’s HTTP Accept-Language header is checked to determine who is the visitor. A cloaked version of the content is served to a crawler instead of the real version.
HTTP_Referer cloaking
This technique is used mostly by hackers to redirect traffic from spam sites to wherever they want their users to land. It is another way of redirecting from one content to another.
Java Script cloaking
Different content is shown to users who have JavaScript enabled in their browsers than to those who have JavaScript turned off (like search engines).
Flash pages
Flash images are shown to human users and keyword-stuffed HTML code is shown to crawlers.
What is cloaking used for?
Once you understand the meaning of cloaking in SEO, then the next question that pops up in your head is why people use cloaking.
Every website owner wants to rank in the search engine. More the traffic, more is the more potential customers. But a search engine is a difficult boss to please.
Cloaking is a faster and shorter route.
An easy way out!
An attempt is made to boost rankings by making search engines believe that the content on the webpage is other than what it is.
It is used to hide or mask fraudulent activities, illegal content, pornography sites, spam sites, ads, or hacking devices. It also hides from competitors, the keywords that the website is ranking for. https://seonorth.ca/seo/cloaking/
When a website is hacked, the hacker can create sub-pages and hide links and keywords in the source code.
Google says No-no!
Why is cloaking not recommended by Google?
Based on the different techniques used, cloaking is differentiated into a black hat and white hat cloaking by specialists. They are at least based on intentions – whether you intend to manipulate search engines.
If you ask Google, no form of cloaking is encouraged. If you are not complying with SEO principles it is bad!
But Matt Cutts said, “White hat cloaking is a contradiction in terms at Google. We’ve never had to make an exception for “white hat” cloaking. If someone tells you that – that’s dangerous.”
He also added that if a website has a code to differentiate a crawler from a user based on an IP address or a user agent, then it is considered as cloaking and Google will take action against that site.
This was a widespread practice in the past but, since then Google and other search engines have evolved and become more efficient in detecting malpractices and penalizing fraudulent websites.
Google has laid out spam policies to help protect users and improve the quality of search results. It also has a black hat combat team that specialized to identify these practices.
If and when a website is caught for cloaking Google can impose a manual action on it, lower its ranking or remove it from the results altogether.
- Google can penalize you.
- Google can ban your site.
- It can ruin your brand name.
What is not considered cloaking?
There are some practices that are like cloaking but are not prohibited. Let me stress that there are no white hat-cloaking techniques. But certain practices are not exactly cloaking, and will not attract a penalty from Google.
“In regards to cloaking, the cloaking team mostly tries to watch out for situations where you’re really showing something to users as to Googlebot.
And with regards to ad clocking or another kind of thighs where it’s like you have to be logged in to actually see the content and that’s kind of different.”
Geo-cloaking:
This method is intended to enhance the user experience by presenting different web pages to users from different geographical locations. Google appears differently to an Indian user than a user who is in the US.
Rewriting URLs:
This process is used to change the appearance of a URL to improve readability and insert target keywords for SEO without altering the content of the web page. This is used in Affiliate marketing.
Flexible Sampling:
In this method, users are able to view the first page of content by clicking on a listed page on Google without subscribing to the host site.
Device-friendly versions:
If you have made different versions of a website to fit desktop and mobile devices separately, it is not considered cloaking.
How to detect cloaking?
Even if you are not practicing cloaking in SEO, it is good to be aware If you want to check if a website is cloaking, you can do that by looking at its source code to see if it is showing different versions of the content to Googlebot.
By comparing the SERP result to the actual web page.
When you see a link in the search results, you see a portion of the description pulled out from the page. You should find that description somewhere on the page, if you don’t, it is suspicious.
By using an online cloak checker.
You can use Webmaster tools that are available for free online and quite effective. For example SiteChecker, and Duplichecker.
Look for other tell-tale signs.
There may be keyword stuffing, irrelevant backlinks, low-quality content, etc. Though they don’t guarantee that cloaking is involved, it is likely that the site is implementing malpractices.
Wrapping up
So, that was about cloaking and why it is a black hat technique.
Intention to deceive or not, if it is declared a prosecuted practice by Google and other search engines, I would say it is safest to steer clear of such practices.
Because the road to hell is paved with good intentions.
It is not enough that you mean good, you need to do good. Though it sounds very much like a philosophy lesson, I am purely talking about SEO.
If you feel the need to cloak, there must be something fundamentally wrong with the site. These issues need to be resolved first to improve your site and enhance user experience. It is not worth investing in quick gains and shortcuts only to be banned or penalized.
There are ample other options in SEO to gain organically with a much-guaranteed return on investment.
What practices would you rather follow than use black hat techniques?
Let me know in the comments.


