Have you ever been in a situation where the other person uses a word in a completely wrong sense and context, and you can’t do anything about it but nod with a sheepish smile?
It happens a lot with me and the term “SEO”.
It’s one of those terms which sounds very sexy and cool so people like to sprinkle it in conversations just to sound smart.
And most “digital marketers” like to slap it on their resumes and profiles because why not?
I don’t blame them or anyone for that. It’s not their fault.
You see, the SEO industry is almost like the stock market industry.
Everything is almost intentionally made to sound complex.
Heck, even the name SEO or Search Engine Optimisation makes it seem like it’s from a dystopian future when it’s clearly not.
I am very tempted to draw a conspiracy theory claiming the “SEO Illuminati” wants to keep it that way because they want to control the mammoth billion-dollar SEO industry out of which $80 billion is in the US alone!
So here is my attempt to free the people from the clutches of the evil “SEO Illuminati” and bring a fresh new perspective to what SEO is, how it works and why you should learn SEO.
Here we go..
What is SEO?

SEO stands for Search Engine Optimisation, and at first glance, it makes you feel like you are trying to optimise the search engine itself or you are optimising for the search engine.
Both are incorrect, and that’s probably the root of many of the misconceptions around SEO.
Allow me to explain.
You see, whenever you need specific information, you head to Google and type in your query, and Google promptly comes back with a page full of results.
Usually, you will notice that there are about ten results on the page but have you ever wondered on what basis do these results appear the way they do? I am sure you have noticed that there is a hierarchy of results starting from 1 to 10.
And that’s what SEO is all about: trying to get your website to the top of the results.
Search Engine Optimisation is the art and science of persuading search engines such as Google to recommend your content to their users as the best solution to their problem.
And here, I would like to bring your attention to the most crucial part of the definition: “solving user queries”.
Every time your users head to Google with their problems and hit in their query, it’s your job to provide them with solutions to their problems in the form of content.
But a lot of people out there focus on the “optimising your website” part more than the “solving user queries” part.
In fact, I emphasise so much on the “solving user queries” part that I would like to rename SEO to UXO or User Experience Optimisation because that’s precisely what you are trying to do: enhancing the experience of your users by solving their problems and making their lives better.
And this is important because, at the end of the day, these users become your customers, not the search engines.
Remember, users have credit cards and bank accounts, not search engines.
And so your focus should always be on optimising for the user and not for the search engines. In fact, even Google expects the same from you.
You see, Google is not a content creator; it’s just a search engine. It needs people like you and me to create content for its users, so in essence, Google needs you more than you need Google.
And it’s funny because the more you optimise for the users, the more Google will love you. After all, Google wants to make sure their users always have the best experience through you and come back for more.
But how do you do SEO then?
For you to have a clear understanding of how SEO works, you need to first understand how search engines work.
How do Search Engines Work?
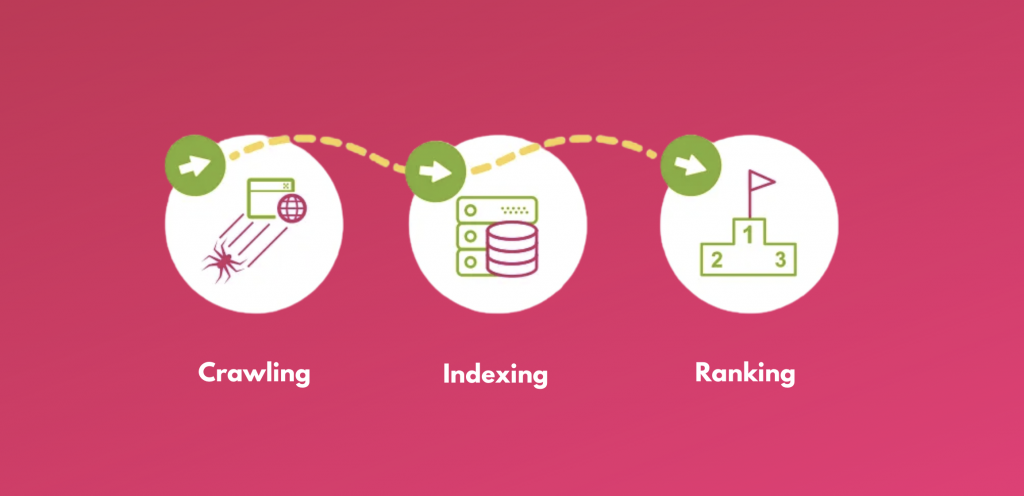
Search engines are amazing creatures, and they work very hard in three main stages: Crawling, Indexing and Ranking.
Let’s understand each step clearly.
Crawling is the discovery process in which search engines send out a team of robots called spiders or crawlers to find new & updated content.
Once these spiders have crawled the internet and returned with either fresh or updated content, Google then tries to understand what the content is about and then goes on to store and organise the content during Indexing.
And when a user types in a query, Google tries to find the most relevant answers from its index based on several factors and provides it to the users in the last stage called Ranking.
Now, based on some data revealed by Google itself and some other anecdotal data, we know there are about 200 different ranking factors based on which, Google decides how and where to rank a particular page of content.
To make things easier for you, I have bucketed these 200 different factors into three main categories:
Relevancy, Authority and User signals.
Relevancy: Google will first check how relevant is the content on the page to the search query of the user? It does this by checking whether the search query itself or the variations of it, is present in the content.
Authority: Now, for every search query, you won’t have a single result but multiple results which might be relevant. Google then tries to decide, among all the relevant results, how authoritative and credible a page is.
User Signals: To make sure that Google is getting the first two categories right, it also looks at user signals and sees how users are interacting with a particular page.
If you want to understand these ranking factors in a detailed way, I strongly recommend you take a look at this amazing infographic:

If you are still confused about how search engines work, a very easy way to understand this is to imagine how a library (remember those?) works.
A librarian would go out there and try to collect and procure all the available books that are there (Crawling)
Then, he/she would come back to the library, organise the books based on different genres like fiction, non-fiction, history etc. (Indexing)
And when a user comes and asks something like “Hey, can you please recommend a really good non-fiction book”, based on several factors the librarian will then recommend the best possible book and tell the user where to find it (Ranking)
And that ladies and gentlemen is how search engines work.
Now, a lot of people equate only the last part, Ranking, with the whole of SEO. As you might have realised now, SEO is more than just ranking.
You need to focus on getting your content discovered (crawled) and organised (indexed) correctly so that it can rank well and get you the organic traffic you deserve.
Speaking of traffic and search engines, let’s try to understand how to optimise for your users and use the search engines to attract them.
How to do SEO?
I want to reiterate: You are optimising for the users and using the search engines to attract them.
What you are doing is user experience optimisation more than anything else.
So to optimise your user’s experience, you need to understand their journey, their problems and challenges so that you can provide the best possible solution in the form of content.
As discussed earlier, the ranking signals can be put into three main buckets: relevancy, authority and user signals and the most fundamental among these is relevancy.
Don’t believe me? Here is a screenshot from Google itself:
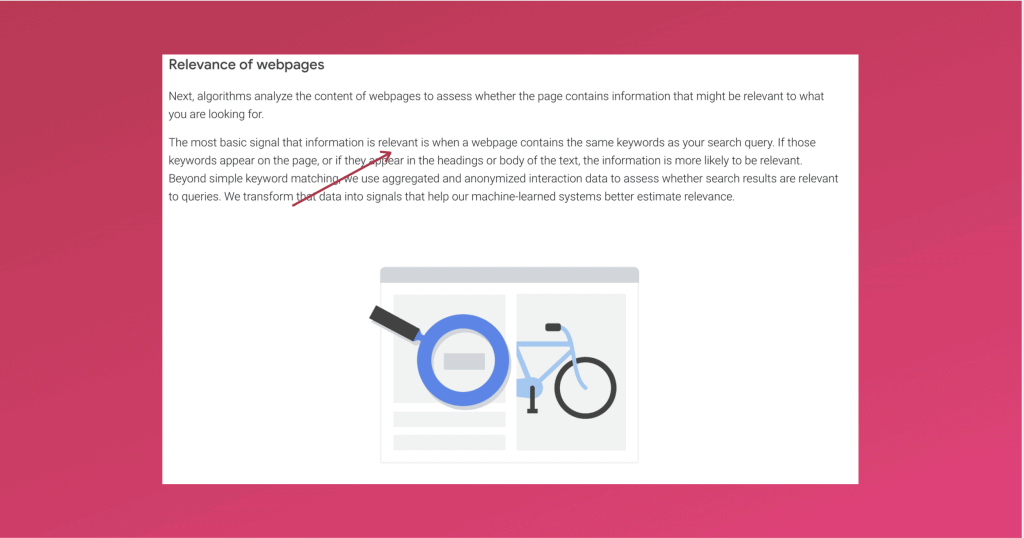
As you can see, if your content is not relevant enough, nothing else matters. The first thing you need to do to get your house in order is to make sure your content is as relevant as possible to the search query.
If that’s the case, would you agree that to make your content as relevant as possible, you first need to know what the search queries are?
Enter Keyword Research.
Stage 1: Keyword Research
Keywords are the words and phrases that people use in search engines. It will allow you to identify words that are popular and make a decision on what to rank for.
Keyword research allows you to answer two crucial questions:
What are people searching for?
How many people are searching for it?
How is it going to help you ask? I am going to take the help of the legendary Peter Drucker to illustrate my point. Here’s what he had to say about marketing:

I believe that this is one of the most accurate understandings of what marketing truly is.
And that’s precisely what you should strive for with keyword research too.
By understanding what people are looking for and how many of them are looking for it, you will be able to create valuable content that fits your users’ needs and sells itself.
Keyword research is user behaviour research, and that’s why I say, keyword research is 50% SEO. Choosing the right keywords is half the battle won. Why?
Because in SEO, not all keywords are equal and choosing the wrong keywords means sabotaging your SEO efforts.
What do I mean by “wrong” keywords? For you to understand this, you need to understand the head and tail of keywords.
The most important thing that you need to look for in a keyword is the intent behind that keyword. What is the intention behind someone searching for a particular keyword and whether the intent is clear in the first place?
To help you understand, let’s use the example of headphones.
When someone types in “headphones” in the search engines, what do you think is the intent behind it? It’s not very clear, is it?
You cannot be sure whether the person is looking for information regarding headphones or wanting to buy a pair of headphone or just researching about headphones.
Now, let’s go a step further and assume that someone is searching for “noise cancellation headphones”. Although the intention is slightly more clear, you still don’t know whether the person is looking for information or has an intention to purchase headphones.
Let’s take this further and assume that the same person is searching for “best noise cancellation headphones under Rs. 20,000”. See the difference?
The intent is much more clearer here, and it’s easy to understand that the person is looking for very specific information here.
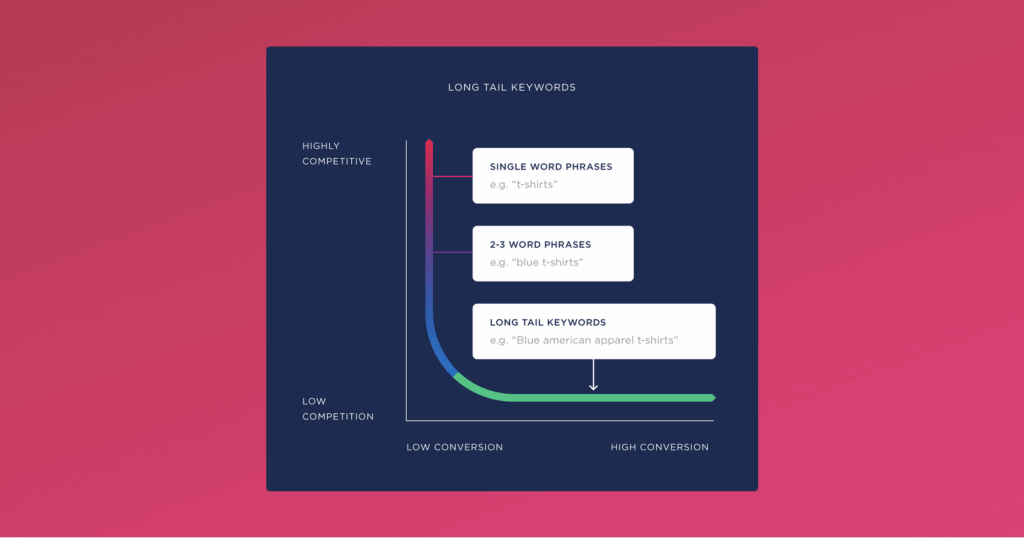
In keyword research, a keyword like “headphones” is called a head keyword and a keyword like “best noise cancellation headphones under Rs. 20,000” is called a long-tail keyword.
If you are getting started with SEO for any website, it’s always recommended that you start off with long-tail keywords. Why?
Because long-tail keyword traffic will not only be more specific, thereby giving you better conversions, but it also means that the competition will be very low, thereby allowing you to rank better and easier.
Here is a quick diagram to help you understand the head and tail of keywords:
But how do you perform keyword research?
There are plenty of tools out there to do this job. You can quickly get started with the Ahrefs free keyword generator tool, or you can also use Uber suggest or SEMrush (which has a 14-day free trial)
These tools will not only help you understand what people are looking for and give you excellent suggestions but also help you give you the search volume (number of people searching that term every month) along with the competitive landscape of those keywords.
The paid version of both Ahrefs and SEMrush is extremely powerful and gives you a lot more information about every keyword, but if you are just getting started, the free version is more than enough.
Read: The Lazy Man’s Guide to (Advanced) Keyword Research
Now that you know what people want and are looking for, what do you think is the next logical step?
Create content.
Stage 2: Create Amazing Content
I can almost feel you freezing in fear the moment I ask you to create content.
If it makes you feel any better, you are not alone.
Almost everyone (including me) reading this post will have, to a certain degree, the irrational fear of creating content.
And this fear stems mostly from the fear of rejection and ridicule and manifests itself as questions like “what should I write about?”, “will people even read it?”, “how to structure my content”, and more.
Like I said before, with SEO, you are actually being a problem solver. Thanks to keyword research, you now know what problems people have. All you have to do now is create solutions in the form of content.
And if your solution is practically useful and valuable enough, it will attract the right people, which will then attract the search engines which will then attract more people.
But how do you articulate this solution of your so that it has the maximum impact?
Here, hold my imaginary beer and allow me to show you the six step content writing framework I have created.
As the name suggests, the framework has six elements that you need to take care of:
- The Headline
- The Introduction
- The What
- The Why
- The How
- Conclusion
Let’s dissect each element now.
1. The Headline: This is the most crucial aspect of your content piece. Not only will it provide a structure for you to create content, but it can also make or create your content.
You see, the headline is the first point of interaction between your users and your content. Your headline is what attracts your audience, sets the expectation and creates curiosity.
If it can’t do that, you are not going too far with your content.
Do yourself a favour and write 20-25 headlines for each piece of content. (you read it right)
Trust me; you will thank me later.
As David Ogilvy said:

2. The Introduction: If the headline’s job is to attract attention, the introduction’s job is to retain it.
Start with a shocking statistic, a story related to the topic or a thought-provoking question. Then, paint a picture as to why this piece of content exists and how it is going to help the reader.
3. The What: This is where the body of the content starts.
In this section, describe the problem the user is facing. This will make the reader feel empathised and helps you build rapport.
Then go on to describe all the things that the reader has tried to solve his/her problem and why it failed.
And then present your solution to their problem.
4. The Why: Just because you have a solution for a problem, doesn’t mean they are going to accept it.
They will have various objections for it, and you need to use this section to address them.
Describe why your solution is probably the best solution for their problem.
5. The How: Now that they are convinced, demonstrate how they can implement the solution in simple and easy steps.
Notice how I used the word “demonstrate”? I mean it.
Your solution should be practical enough for your users to find it useful, or they will bounce right back to where they came from.
6. The Conclusion: End it with a quick summary of what they learnt, the possible pitfalls they might encounter and a call to action.
My favourite call to action is to get them to comment on what they thought about the content that they just read. User-generated content allows you to add more depth to the already in-depth content that you have created.
And that’s it! Thanks to your fantastic content, you have made your reader’s life that much better.
Great! But remember this: break the framework the first chance you get.
These are training wheels for you to get started. Once you understand your users more, you will be able to craft content that not only gets read but also shared.
Now that you have some content let’s move on to the next step: On-Page SEO.
Stage 3: On-Page SEO
Did you notice that I made no reference to SEO in the previous stage? I did that for a reason.
When you are creating content, always make it for the users. If you provide enough value, you will attract your audience, and then the algorithms will follow.
And once the algorithms follow, you have to make sure you help them understand what your content is all about.
And that’s where On-Page SEO comes into the picture.
If you remember clearly, I had mentioned that the rankings signals of Google could be broadly divided into three buckets: relevancy, authority and user signals.
On-Page SEO is all about relevancy.
You now know what people are searching for and you have created content around it too. Now, it’s time to increase the relevancy of the content to help search engines understand and organise your content.
There are six different elements of On-Page for which you can increase the relevancy:
- Title tags
- Meta description
- Header tags
- URL
- Images
- Content
Let’s go one by one and understand each of these elements:
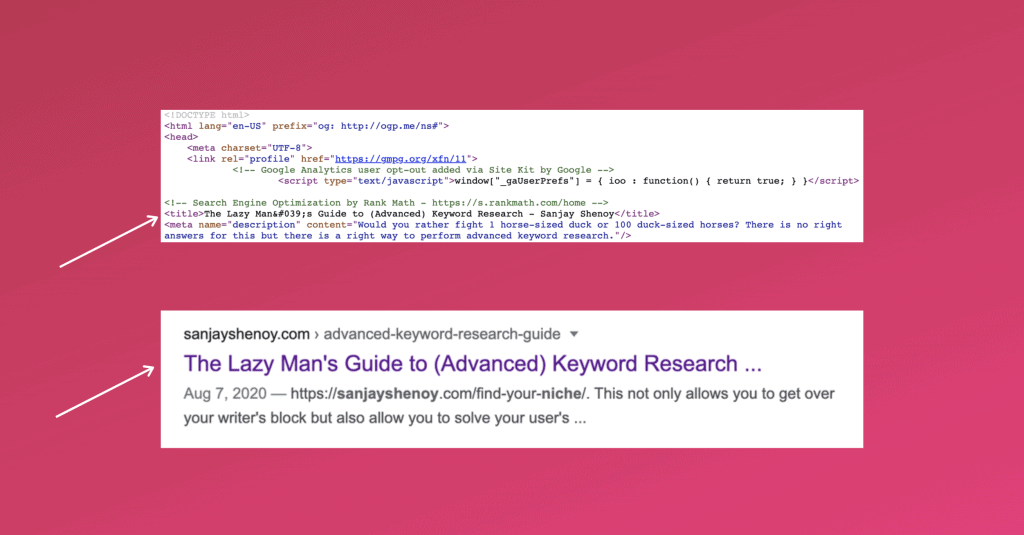
Title tags: A title tag is the HTML element used to specify the title of a webpage.
It is a powerful relevancy signal, and you have to make sure that your keyword is in it. But there is a catch.
Your title needs to be less than 60 characters (or 600 pixels) with the keyword in it. I know it doesn’t sound like a lot, but trust me, you can create unique titles in 60 characters.
Basically, the headline of your content can be your title. All the effort you put in creating that amazing headline should now be optimised to include the keyword in it.
This is how the title tag looks like:
Meta description: The meta description is an HTML attribute that provides a brief summary of a web page
Ok, I’ll be honest here. Meta description is not a direct relevancy signal, but they do have an impact on the click-through rate (CTR) which then has an indirect impact on your ranking.
You will also notice (refer screenshot) that even if you explicitly specify a meta description, Google sometimes does not consider that and create its own from fetching it from your content.
But it’s still a good idea to write a nice catchy meta description, and you have about 160 characters. So make sure you include your keyword here too.
This is how the meta description looks like:

Header tags: These are considered secondary title tags and are used to differentiate the headings and sub-headings of a page from the rest of the content.
Header tags have a hierarchy and go from h1 to h6. h1 tags are reserved for the heading, and all the subheadings need to be wrapped in h2 all the way to h6.
Headers tags are super important because they create information hierarchy both for users and crawlers, which is why the relevancy weightage is relatively high for these tags. So make sure you include your keywords in all the header tags on your page.
Here is how different header tags look like:
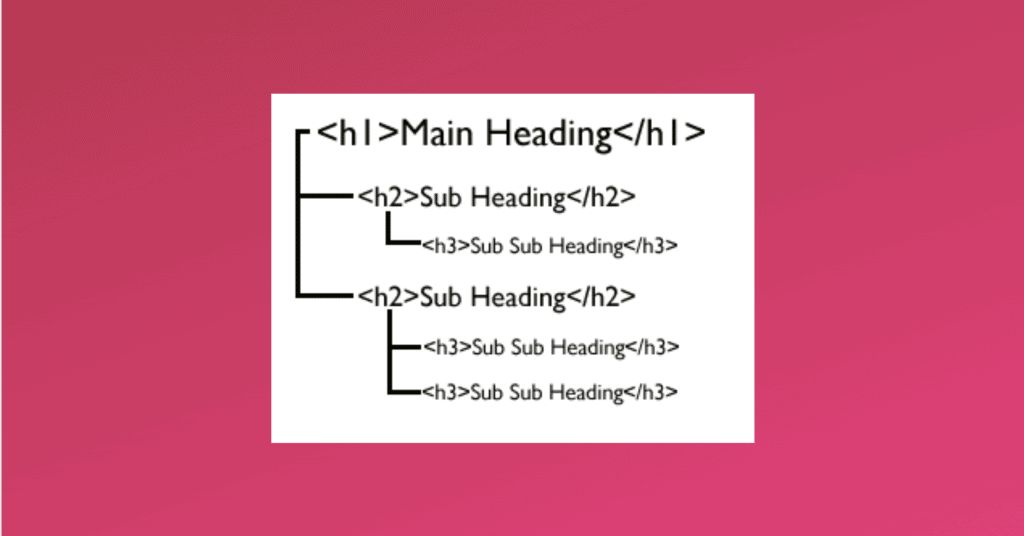
URL: URL stands for Uniform Resource Locator. It is basically the link or the address of a web page.
You need to use keywords in the URL too, but there are a few caveats.
First, avoid using stop words like a,the,of,or etc in URLs. They make the URLs unnecessarily long, which is bad for your SEO.
URLs are also case sensitive, so it is always recommended that you keep them in lower case to avoid any confusion. Underscores and spaces are a complete no-no as they make the URLs confusing and ugly to look at.
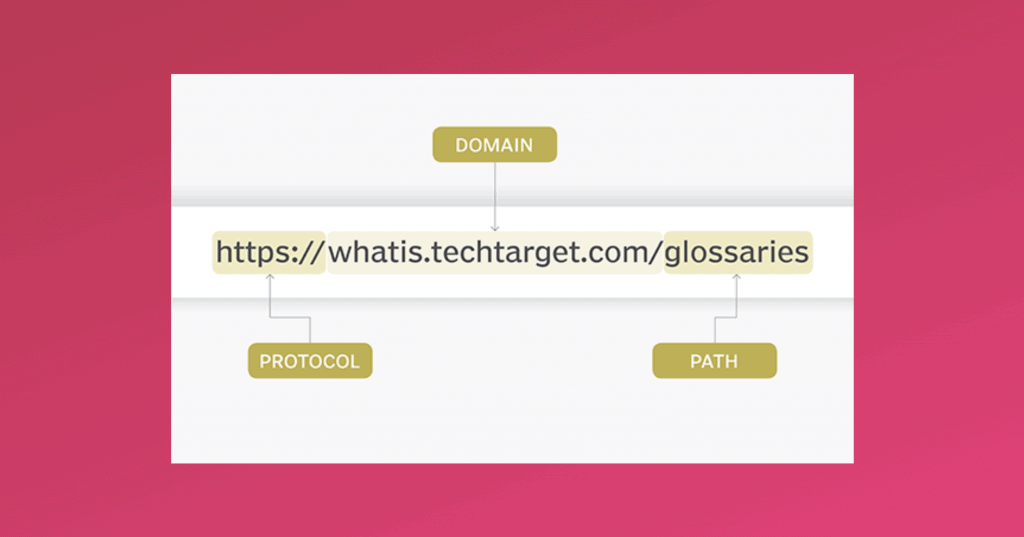
Images: As cliched as it may sounds, pictures are indeed worth a thousand words.
From an SEO perspective, not only do they break the monotony of text but also give you extra real estate to increase the relevancy of your page.
To achieve that, include keywords in your alt tags, and another good option would be to change the file name of your images to your keywords.
And as a bonus, you might end up getting a decent amount of traffic from the images search engine too so don’t ignore images.
Content: And of course, the biggest real estate to increase relevancy is your content itself.
Make sure you include your keywords in your content but for the love of God, use them naturally and make sure it’s grammatically correct.
This is why I kept this part in the end because I have seen this more times than I would like when people stuff their content with keywords which do not make any grammatical sense.
Always remember, optimise for the users, the search engines will follow.
Now that you have used every inch of your digital real estate, it’s time to increase the authority of your website.
It’s time to do some off-page SEO.
Stage 4: Off-Page SEO
Have you ever wondered what made Google the number 1 search engine in the world?
It definitely wasn’t the first search engine to be built, there were plenty of search engines that were built before it and plenty more after it, but how did Google manage to reign supreme?
Google realised that the job of the search engine is not to just crawl and index every available content on the internet but also make sure users get quality results.
You see, just because you have 25 million results for a single query doesn’t mean that you are going to go through all the results. You will still be looking for your information in the first ten results.
This is the part most other search engines missed out on – quality results and Google achieved this with the legendary PageRank algorithm (which is still in use).
The PageRank (named after Larry Page) allowed Google to understand the relative importance, authority and credibility of a certain page. And how did it decide this? Backlinks.
Using links from other websites as a measure to gauge the importance of a page proved to be a game-changer. This was the same concept used in academic papers too. If a certain academic paper has been cited enough times in other academic papers, you would know how authoritative that academic paper is.
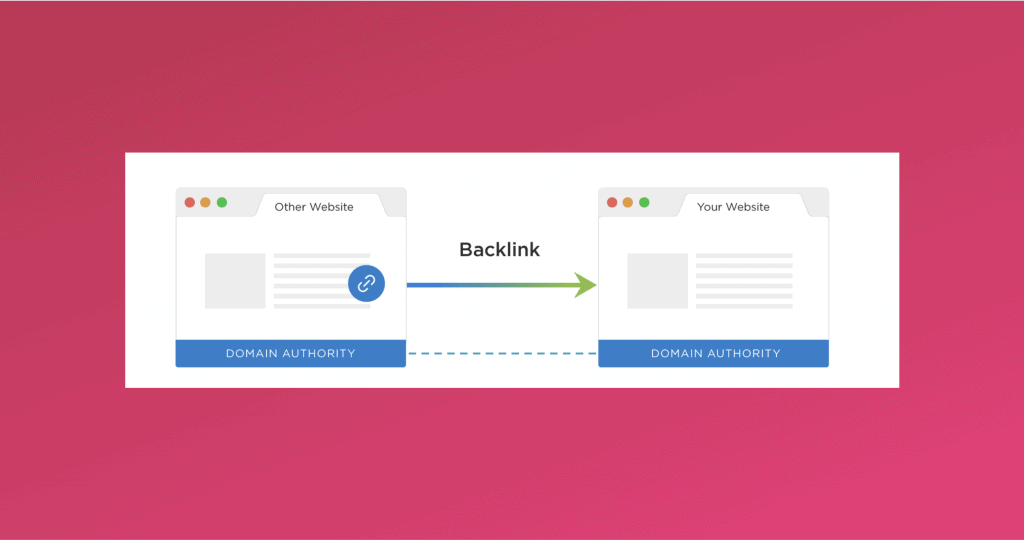
But what is a backlink?
A backlink is an incoming hyperlink from one website to another. If website A has linked out to website B, then you can say that website B has got a backlink from website A. In other words, when a link is placed to your website from another website, it is called a backlink.
This is how it looks in HTML:
<a href=”https://sanjayshenoy.com/”>Sanjay Shenoy</a>
This is how the link looks like:
A backlink is a vote of authority and credibility from one website to another. The more relevant quality votes you get, the better results you have. To understand further, you need to understand the concept of link quality and link juice.
Thanks to the PageRank algorithm, every page will have a quality score called PageRank. This score ranges from 0-10, 10 being the highest.
So the idea is that you need to get backlinks from high PageRank (PR) pages as much as possible. Higher the PageRank, more powerful the backlink will be.
Unfortunately, PR data is not publicly available anymore (although still very much in use), which means you cannot truly gauge the quality of a page.
But, there a lot of third party metrics like Domain Authority and Page Authority ( DA & PA) from Moz, and Domain Rating and URL Rating (DR & PR) from Ahrefs which try to mimic PageRank and give you a sense of how authoritative a website and a page is.
Now, this authority can be passed around from one website to another through backlinks. People refer to this concept as link juice.
Link juice can loosely be interpreted as the authority that one website passes on to another. A good way to understand link juice is to picture websites as water tanks.
Let’s assume there are three websites represented by water tanks. Higher the PageRank of a website, bigger the water tank is going to be. So let’s assume that these three websites have PageRanks of 7, 5, and 3 and the PR 7 & 3 websites are linking to the PR 5 website, represented by the pipes.
So when the PR 7 and PR 3 is linking to a PR 5 website, it can actually pass on the link juice to fill up and increase the authority of the PR 5 website. I used this example to illustrate that authority can flow both ways; it need not have to come from a higher authority website only.
(BTW, the term link juice is not an official term and is a crude representation but it really helps to understand how authority works)
Eventually, a lot of website owners wanted to control the flow of this link juice. Basically, they wanted to add a tap to the pipes to control the flow.
So Google, along with other search engines, came up with a simple, yet effective solution called the “no follow” attribute. This simple HTML attribute, when added to a backlink was the equivalent of closing the tap to the pipe, meaning the link juice would not flow.
And if the “no follow” attribute was not there, it was considered to be a “do follow” link, or a link with the tap open, by default.
So does that mean a no-follow link is useless? Not really.
A no-follow link is still considered as a signal but not with the same weightage as a do-follow link. But, a no-follow link still helps a lot in another aspect – anchor text.
The anchor text is the text with which you wrap the link. Here is how it looks in HTML:
<a href=”https://sanjayshenoy.com/”>Sanjay Shenoy</a>
The bolded words are the anchor text. Anchor texts are important because Google believes that anchors tell search engines a lot about the page than the page itself. In other words, it was a relevancy signal wrapped around an authority signal.
But not soon, all the SEO guys started abusing this by wrapping their links with the keywords they were trying to rank as their anchor text.
And this is when Google released the Penguin update to fight anchor text spam.
So to make sure you are in the good books of Google, you need to have natural, diverse backlink and anchor text profile. A good backlink profile will have :
- Backlinks from unique websites
- Relevant to your website
- High Authority
- A healthy balance between do-follow and no-follow
- Diverse anchor texts
Great, now that you have amassed all the authority you need, let’s move on to technical SEO.
Stage 5: Technical SEO
Technical SEO is where you make your website more crawl-able, and thereby more indexable, and improve its speed and credibility to rank better and efficiently.
As discussed before, search engines crawl, index and then rank your content based on the search query. So, to rank better, you need to get indexed better, and to get indexed better, you need to get crawled better.
To understand how a crawler is crawling your website, you can primarily use two tools:
- Google Search Console – Coverage Report
- Screaming Frog
Google gives you enough information in the coverage report to help you understand how the crawlers are actually crawling your website.
The coverage report will give you information regarding four main elements:
- Errors – pages which might throwing server errors or 404s.
- Valid with warnings – pages that are indexed but might still have problems
- Valid – all the pages from your website that has been successfully crawled and indexed
- Excluded – pages that have not been crawled and indexed for various reasons
So the idea here is to make sure you have all the important pages from your website under “valid”, and all the sensitive and unimportant pages are “excluded”
If you have any errors or warnings, make sure you fix them and keep these sections clean.
Now, you can go a level deeper and actually see how a crawler “views” your website thanks to Screaming Frog. This is an amazingly useful desktop tool which crawls websites’ links, images, CSS, script and apps from an SEO perspective.
And it looks something like this:
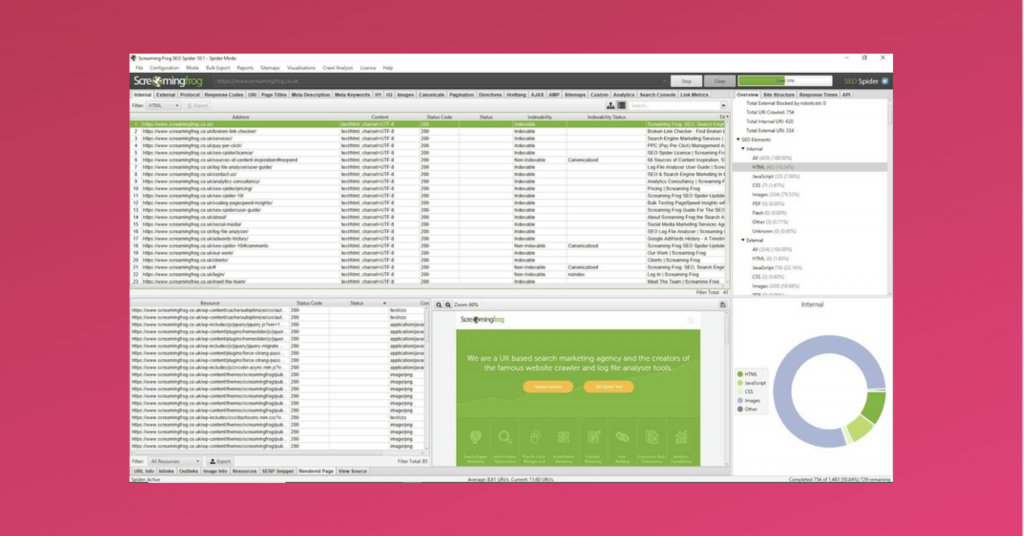
This tool can again be used to find pages that might have issues and also to make sure all the on-page elements are in place for all the pages.
The best part is that this is a freemium tool and the free version allows you to crawl up to 500 URLs which should be enough for a new website.
Once you have identified any potential issues and fixed it, it’s a good idea to create a list of instructions that all the crawlers need to follow when they visit your website.
And that’s what your robots.txt file does.
Robots.txt
Robots.txt, as the name suggests, is a simple text file which tells a search engine where it can and can’t go on your website.
Every crawler out there, when they visit your website, your robots.txt is the first page they will visit. The robots.txt will have a set of instructions for every crawler as to which page they are allowed to crawl and index and which ones they should ignore.
Now, why would you want to ask the crawlers NOT to crawl certain pages?
Well, for starters, you would want to keep your sensitive areas like the admin area, members area etc. not to be crawled and indexed, thereby making it less vulnerable to attacks.
But more importantly so, it is done to optimise what is called a crawl budget.
You see, it takes a lot of resources to run crawlers 24X7 for search engines which is why they have an allowance for each website.
This means that the search engines do not crawl every website equally. For example, some websites might have a crawl budget of 100 URLs, and another might have a crawl budget of 20 which means that every time the crawler visits these websites, it will only crawl and index 100 URLs and 20 URLs from your page.
So, if these websites have a total of say 150 and 40 URLs, 50 and 20 URLs from these websites might NOT get crawled at all and thereby not get indexed and ranked.
Now, what if your important pages were part of these 50 and 20 URLs? You wouldn’t want that to happen, right? Which is why, you make sure, through the robots.txt, you block all the unnecessary and sensitive URLs so that the important URLs get the crawl budget they deserve.
Here is how my robots.txt looks like:

As you can see, there are four main elements to the Robots.txt file:
- User-agent: Each crawler has a name (e.g. Googlebot), and you can use this to give specific instructions to specific crawlers
- Allow: Here you can mention all the pages that are allowed.
- Disallow: Here you can mention all the pages that are not allowed to be crawled.
- Regex (*): This is like a wild card and when used it means it applies to all
But when it comes to getting all the important pages crawled, robots.txt is not enough. We need something called XML sitemaps.
Sitemaps
When a website grows, so does the number of pages in it and this can lead to what is called as “orphan pages”; pages that are not linked from any page.
And these orphan pages can be tough for the crawlers to find. To ensure this does not happen and also to make sure all the necessary pages are crawled, we use an aptly named file called as a Sitemap.
Let’s say what Google has to say about sitemaps:
A sitemap is a file where you provide information about the pages, videos, and other files on your site, and the relationships between them. Search engines like Google read this file to more intelligently crawl your site.
I couldn’t have explained what a sitemap is, better than what Google has.
The good news is that plugins like YoastSEO and Rankmath automatically create sitemaps for your WordPress websites.
But it is good practice to submit your sitemaps in your Google Search Console here:
Having said that, apart from sitemaps, it’s always a good idea to interlink your pages for better crawl-ability and also better user experience.
Page Speed
Another not so surprising metric that Google uses is page speed. How fast does your website load for your users?
A good place to check how fast your site is loading is PageSpeed insights tool.
But page speed is not just about how fast your website will load but also how is it going to affect user experience.
For now, Google will be using three main metrics to measure this:
Largest Contentful Paint (LCP): This metric measures your loading performance. An LCP under 2.5 seconds is considered to be good.
First Input Delay (FID): This helps you understand interactivity and user experience, and ideally, it should be less than 100 milliseconds.
Cumulative Layout Shift: This helps you understand visual stability or in other words how stable all the elements like your text, images etc. are on your website and you should maintain a CLS of less than 0.1.
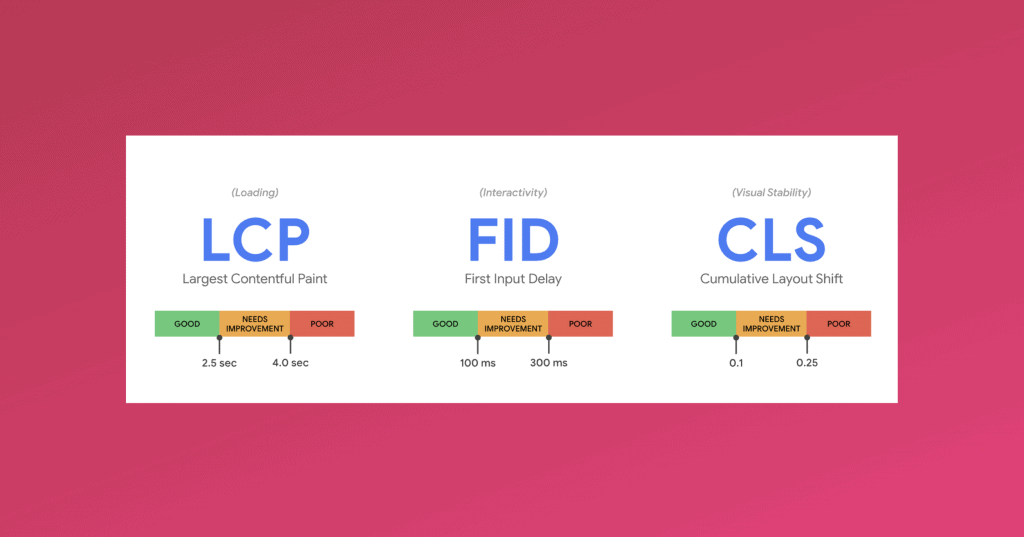
You can find all of these metrics in PageSpeed insights tool and also in your search console. Here is a screenshot of all these metrics for this page:
But how to improve PageSpeed Insights scores?
First, get yourself better hosting with a Content Delivery Network (CDN). My recommendation for WordPress websites is WPX hosting. They are considered to be the best in business with unmatched support and probably why I use it too.
Second, use a caching plugin like W3 total cache or SWIFT performance (I use this) to tweak a few settings to make your site lightning fast.
Third, especially if you are on WordPress, use a good theme like Astra, which is light and not bloated and also helps you in user experience.
Awesome! Besides having a fast website, you should also have a secure website.
Secure Website
You obviously would want your website to be secure not just to be safe from attacks but also to make sure your users feel safe.
From an SEO perspective, it’s important that you have what they call an SSL certificate.
SSL stands for Secure Sockets Layer, a global standard security technology that enables encrypted communication between a web browser and a web server.
When you type in the address for any website on your browser, you are actually requesting information from the website’s web server. While this is happening, you might be vulnerable for attacks, especially if you are sending and receiving sensitive information like passwords, credit card information etc.
An SSL secures this communication that is happening between your browser and the web server, thereby keeping you safe from hackers.
SSL certificates are what enable websites to move from HTTP to HTTPS, and there definitely seems to be, although minimal, a positive correlation between better rankings and having an SSL certificate.
You can get yourself a free SSL certificate from Cloudflare or if you have gone ahead with WPX hosting they will give you a free SSL certificate too.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is Black hat SEO & White hat SEO?
Once you get into SEO, you will start noticing the terms black hat and white hat a lot. To simplify it, according to Google, black hats are the bad guys, and white hats are the good guys.
But how does Google decide that?
For starters, white hat SEO is when you perform SEO according to Google’s webmaster policies. Google has laid out, although not too clearly, guidelines you need to follow to in order to optimise your site ethically and correctly. In other words, don’t try to manipulate rankings and optimise for the users and not the algorithms (I told you so).
When you try to manipulate rankings, and you can if you want to, it’s called Black hat SEO.
Again, there is no real consensus as to what exactly qualifies as Black hat SEO. But a lot of people seem to agree that creating duplicate or spun content, stuffing your content with invisible keywords, cloaking, sneaky redirects, buying or exchanging backlinks can be considered black hat.
But then again, there is no clear demarcation in terms of what black hat and white hat is. For example, guest posting, which a lot of people consider to be white hat, can be seen as black hat since you are technically not allowed to buy/exchange links.
Strictly speaking, you are only allowed to earn backlinks with your content. But considering the ridiculous competition and noise out there, it can be an uphill task to get your valuable content found and earn a backlink for yourself.
My suggestion would be not to mess your head with these terms but make sure you don’t do shady stuff, optimise for the user, and everyone will be happy.
How can you learn SEO? Can you learn it on your own at home? Is it hard?
To be honest, how hard or easy it depends on who you are learning it from and how interested you are in it.
If you are not genuinely interested in it and are just trying to jump on to the bandwagon only because everyone is getting on to it, you are going to have a tough time.
Let me be frank; SEO is vast and extremely dynamic too. It’s going to take a while for you to understand every aspect of SEO, and you will never be “done” with learning about it.
I have been into SEO for more than ten years, and I learn something new about it almost every single day.
Having said that, without trying to toot my own horn, this post can be a good place for you to start understanding SEO.
Once you have a clear understanding of the fundamental concept of SEO, I strongly recommend you to go out there and implement it. And the best way to do this is to set up a self-hosted WordPress blog.
Your blog can be the perfect playground for you to try different things with SEO (among other things). Don’t worry, even if you screw up, it’s not like the end of the world. Make sure you have backups that you can revert to if things go south.
So, yes, you can definitely learn SEO on your own, at home with the unlimited resources available on the internet but your learning curve can be dramatically flattened if you learn from a good reliable source.
Does SEO work? Is SEO dead?
Ugh! I am so sick of this question, to be honest.
I have been hearing this since I started way back in 2009 and for some reason, it doesn’t seem to stop.
SEO definitely works and is alive and kicking.
But SEO is continuously evolving.
What used to work 10 years ago obviously will not work today. The search engine has evolved dramatically and understands users way better but still allows webmasters to leverage the enormous potential that it offers.
Try it for yourself, and you will be surprised how effectively it can work if you are patient and consistent enough.
Do you have to know coding to learn SEO?
Honestly, it definitely helps if you know how to code, but you don’t necessarily have to.
I don’t know how to code, and I seem to have been doing just fine for over 11 years now.
And frankly, “coding” is a very generalised term here. You can learn web technologies to help you with SEO, or languages like python to help you with runnings scripts and other languages to help you with data.
It’s endless, to be honest.
But remember, SEO is more of a marketing function than a tech function. You have to be a marketer first and then a coder if you have to succeed in search engine optimisation.
Conclusion
And that ladies and gentlemen is how to perform search engine optimisation for your website.
I know all this information might seem overwhelming for you, but I would like to tell you that it’s normal to feel overwhelmed.
It took me about ten years to wrap my head around all of this. Hopefully, I have made it easier for you by addressing all the important aspects of SEO.
And like I always say, Search Engine Optimisation is actually User Experience Optimisation. SEO is a misnomer and makes you believe you are optimising for the search engines, when in fact you are optimising for the users.
You need to understand that Google is not a content creator, but you can be. So Google needs you, more than you need Google.
Your job is to solve your users’ problems so well that you make Google obsolete. And that ironically is how you win at search engine optimisation.
Do you have any questions? Let me know in the comments below.



![A Practical Guide on How to Become a Content Writer in India [2023] – Sanjay Shenoy](https://sanjayshenoy.com/wp-content/uploads/2020/03/How-to-become-a-content-write-in-India.png)
Dear Sanjay,
Very nicely articulated about SEO and was very informative and explained in detail.
It will definitely help me to build my website which I have launched recently and I am sure by being your student for and learning from the workshop of “Writers Bloc” will add value to my SEO journey to a great height.
Thanks once again.
Glad you liked it Pankaj!
Good one Sanjay!
However it will be more helpful if you can create more internal links on how and from where to add meta description, titletags, how sitemap can be created and edited and the other technical aspects.
Great information Sanjay! And the way you explained, SEO seems not do tough though. Thanks.
Experienced good information though some content was not very clear as I have just begun the digital learning. Still got a very clear picture . Liked the content .
Enjoyed the learning.
Thanks Meenu! Would you mind telling me what exactly you didn’t understand?
Thank You brother
Thank you!
The motto of your blog is “Digital Marketing made Easy” and this post does make understanding SEO easy.
I loved how you explained the crawling, indexing and ranking terms with that of a Librarian and how she arranges collects & arranges the book and recommends according to need.
Another highlight was How you always say to form a bucket of keywords for post and write about 100-200 words for each of them, which will make the post much more relevant and will give the post a chance to rank higher. I observed you did the same thing and used different terms to form cluster of keywords and optimised your post.
Even after using the keywords you didn’t deviate from User Experience Optimisation (I loved the transition) which is all that counts.
I had a great time reading this awesome post. Thank you Sanjay Shenoy for making everything simple.
Thanks Ankit! Trying my best every day to simplify everything related to digital marketing and make it more accessible to people.
I always practice what I preach Ankit! And thanks for your comment.
Amazing ..thanks for sharing
A well written post. Got a good idea of the term SEO
AMAZING stuff. A complete guide on SEO, like an E-course in itself if one can understand, consume and implement the value shared over here. And I always like the way you focuses more on content and relevancy for audience rather than just technical stuff.
Thanks Sanyam! And yes, I believe people misunderstand SEO a lot and all I am trying to do is bring a fresh perspective.
Explains SEO in a simple language. I like Sanjay’s style of teaching . He uses the same technique while writing also. Overall I liked this article. It explains in detail what is SEO, how it works and how to do SEO analysis of your website in a very articulate manner.
Thanks Anurag! I try to simplify as much as possible and am glad you could appreciate it.
This is well written and in depth. Thanks
Wow wow wow wow wow i did study digital marketing but reading this was best decision ever i made. its like i am listening to you as you talk you made it very easy i think even easy its difficult word i would say very lightly to understand wow wow
Thanks Thabiso! Very happy to know that.
A well structured and easy to comprehend article. If you want to take the path of SEO, start here.
Hello Sanjay sir,
I loved how you explained each point in-depth you explain it very well.
I think this is the best SEO article I had ever read.
After reading the article my doubts are clear regarding SEO, especially the Keyword Research section you explained very well, How SEO Works section, everything you mentioned in the above article is awesome and I think every digital marketer has to must read this blog in his/her life at once.
if any fresher also reads this article his/her so many doubts going to be solved.
Thank you so much Sanjay sir for providing such golden value from your real experience.
Just trying my best Brijesh! Thanks for your support.
Very nicely and briefly explained about SEO,first time I have a very clear understanding of seo.
Glad you liked it Divya!
Thanks for this marvelous pillar content. I think it’s the entire HIIT program in a nutshell.
You’ll always be my guru.
Thanks 👍 again.
Hello sir.
You are awesome. I just become an addict of your content. Keep doing 🙂
Thanks Darshan!
Dear Sanjay,
It’s really an amazing document for me as I thought something else about SEO.
You have given me such a very useful information and also very different experience on SEO perspective.\
Like how I really enjoyed reading your Content Marketing Ebook and the similar way I did enjoy reading and getting to know the concept of SEO.
It really helped and I will try to implement as much as possible.
Thank you so much!
All your ten years of research in SEO, you transformed it in a nicer way!
Thanks Again!
Really great summary of SEO. Just perfect
Well done ! Sanjay sir, so comprehensive and precise. its fulfill brain hunger of seo.
It’s really helpful summary for people related with SEO. Thank you Sanjay sir, for this amazing article.
To be honest, I was feeling very low and demotivated. I have started my amazon affiliate blog 5 months back. I was really hoping to make a good start during the festive season. But I could not make a single sale during ongoing e-commerce sale carnival.
Suddenly got this article link in my email from Sanjay. I have invested my 10 mins to read the whole article. It brought back some amount of confidence. Now I am hopeful again.
Thanks Sanjay.
Best
-Sandeep
Hello Sir,
This is awesome content. Whereas I already knew about SEO but this content gives me in-depth information about this topic. Thank you for this amazing writings.
This is a nice piece of artilcle about SEO with indept explanations.
Thanks.
Very well articulated piece. Got a lot more clarity on many grey areas. Thank you
It’s complete A to Z of On-page SEO.
Very nicely explained. Just loved it.
Thanks
Pingback: The Most Definitive Ahrefs Review (+ 5 Unique Ways To Use It) - Sanjay Shenoy
Thanks, Sanjay for this Amazing Article, Extremely Helpful in clarifying some unanswered SEO queries.
Amazing. So in depth article . Wonder, ever I read this type of article on SEO.
you tried to cover almost everything about SEO in one blog post. It really feels like you come on live on webinar and guiding us through SEO jouney.
Good Job Sanjay,
Really enjoyed the whole article. Fantastic presentation and read it in on stroke. Although i know something about SEO this article was very enlightening . Will surely fall back on this post to clear my doubts during implementation
Nice Information Sanjay
Pingback: The Most Definitive Ahrefs Review (+ 5 Unique Ways To Use It) – Content Chai
Pingback: 21+ Blog Post Ideas You Can Instantly Implement
Pingback: A Practical Guide on How to Become a Content Writer in India
Pingback: The Lazy Man's Guide to (Advanced) Keyword Research - Sanjay Shenoy
Thanks for this in-depth article on SEO. You have greatly simplified it. It’s going to be a year since I started blogging and I am trying to learn about it.
Amazing Article on SEO …..Thank you
Pingback: 10 On-Page SEO Techniques to improve your ranking - Art 2 Blog
Pingback: Basics of Digital Marketing in 10 minutes
Hey Sanjay,
This is one of the diffinitive post about SEO which I ever read. You have covered all the basic and advanced terms of SEO which we should not ignore.
Thanks for providing such informative and detailed guide to make SEO effort easy.
Balendu,
Regards
Sanjay has simplified the technical term SEO and really made it to UXO; user experience optimization.
I have learned a lot, especially keyword research,on-page, technical,off-page & local SEO.
This content is written so lucid that I would like to revisit it again and again.
Cheers,
Love the breakdown Sanjay!!
SEO Guru. Thanks for sharing awesome layman’s guide. Really fantastic. I don’t see anyone doing it and definitely worth reading.
Thank you for writing in-depth content Sanjay,
I got to know a lot about SEO in just a few mins.
I am very happy and I found your blog as an Education Resource 🙂
This is insightful.
So novel way of explanation and crystal clear in making points understood.
A good article covering most of the topics of SEO. Also not getting very technical.
Pingback: Week 0 - Growth Hacking with Vaibhav Sisinty - Your Online Tutor Growth Specialist
I was searching for this topic for a long time and finally found it on your blog. Really detailed article. Thank you so much and have a great day.
Pingback: The Most Definitive Ahrefs Review (+ 5 Unique Ways To Use It) – Sanjay Shenoy
Very insightful article Sanjay. I share the same Niche and, like your website, I find your content very well structured interesting.
Definitely shows the complete experience you have in the SEO Industry in this complete blog, loved the way how you explained all the important aspects of SEO so easily.
Hey thank you for sharing the such a Wonderfull guidance over – How SEO Works
I always believe that SEO is not a one-night game but it’s a long-term game. Keeping consistent and working wholeheartedly makes the game a bit easy. Whatever your article is telling, it’s an ultimate guide and if one can follow the steps, they are getting started with SEO and in future, they will get the results
Pingback: The Most Definitive Ahrefs Review (+ 5 Unique Ways To Use It) - Sanjay Shenoy
SEO is a haunting term utilised in many selective platforms knowingly, in-depth, or even unknowingly. Specific job sites are so crazy of SEO demands than being informative, a stylish approach convincing readers of their top-to-bottom so-called SEO perfection. The way you analysed the subject, sharing your experience, citing simple, understandable examples and expressing with clarity what it means, such as “UXO“ & “Our focus should be on optimising for the user and not for the search engines”, likes are appreciable. Even some SEO Tutors should look into these aspects. Incredible exposure to the subject. Thanks, Sanjay.
Pingback: Digital marketing for business - visionscreator.com
Pingback: Top 10 Digital Marketing Companies in Bangalore to hike business
Hello,
This article is very informative.. liked the way how you explained all the important aspects of SEO so easily. It will definitely help me to build my website…
Thanks…
Pingback: 15 Essential Blog Writing Tips (That Actually Works Best in 2021)
Pingback: 9 reasons Why local SEO is Important?
Pingback: Top 10 SEO Courses in Delhi to stay relevant - Sanjay Shenoy
Pingback: 10 Best Digital Marketing Companies in Kochi - Sanjay Shenoy
Pingback: Top 10 SEO Courses in Mumbai to upskill your career - Sanjay Shenoy
Pingback: Basics of Digital Marketing and 7 Types of Digital Marketing and best social media platforms
Pingback: What are breadcrumbs in SEO? Are breadcrumbs good for SEO? - Sanjay Shenoy
Pingback: WRITE 10 EPIC BLOG POSTS IN 10 WEEKS WITH HIIT CONTENT [WITHOUT ANY EXPERIENCE]
Pingback: How to earn from Content Writing in India with no experience
Pingback: The Top 10 Laravel Development Companies in India! - Sanjay Shenoy
Pingback: Top 10 Laravel Development Companies in India! - Sanjay Shenoy